Follow these instructions to run it manually:
- You do not need photometric or completely dark conditions to run kfindwhm.script. Dark twilight is OK (sun at least 12 degrees below the horizon).
-
Make sure that track and dome are on (Tele Tasks),
then type "kfindfwhm" in the command window. This command is an alias to:
"source /home/falco/findfwhm/kfindfwhm.script."
- The script will first ask you to hit return if you're ready to start and you want to use the default, the r filter. If you wish to use another filter enter its name (from the list the script shows), then hit return. You can quit at this stage by entering X, or if you enter a filter not in the list, the script will also quit. The script will print out some information as it goes, more than you need, but just in case. The script automatically looks for stars not far from zenith at the time of observations, so the telescope should not have to slew very far if you start near zenith.
- The script will take a focus image with 11 10-second exposures with focus values between +70 and -70 focus units, centered on the starting focus value. The script analyzes the focus image for you. The total time to run the script is about 5 minutes. If it's successful, it will print "FINDFWHM RESULTS" and date, best focus, FWHM (in arcsec) and the filter. It saves those values and the mirror temperatures to a running log file (/home/observer/findfwhm/findfwhm.log). It will also set the telescope focus to the best value it found, so there is no need to change the focus after running the script. If it fails, it will print "FINDFWHM FAILED" and a reason for the failure if it knows it, and do nothing else.
Possible causes for failure are:
- Starting from a focus value beyond the range that the script examines. Try focusing the telescope manually first and then run kfindfwhm as described above.
- Clouds may prevent meaningful measurements.
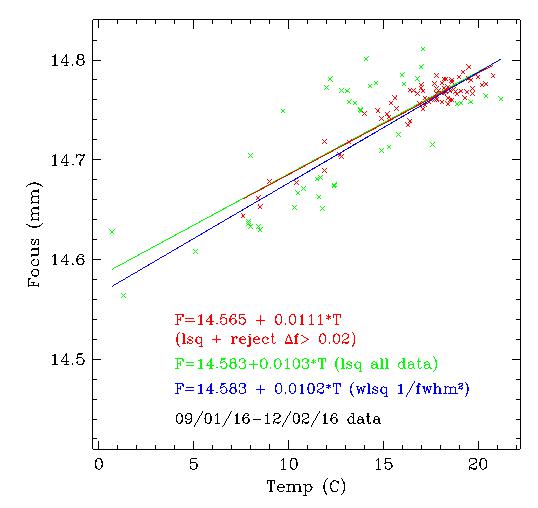
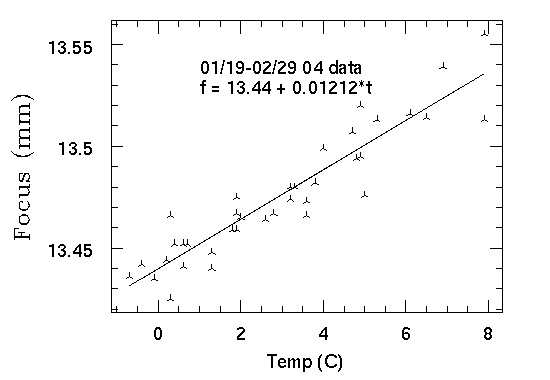
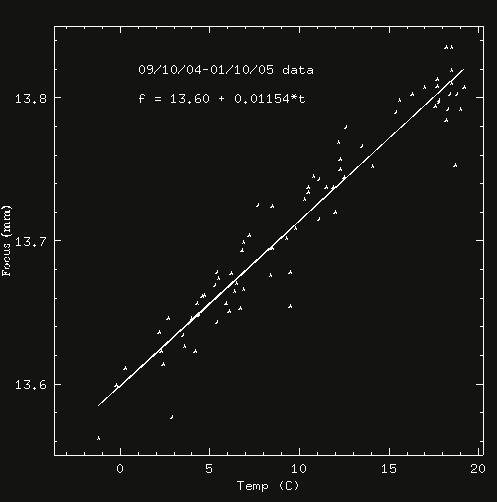
Type "tempfocus" in the Telshell at the beginning of the night to run tempfocus. Make sure that you start out close to focus. To confirm that, first run kfindfwhm once as described above. You may also type "deltafocus" after you've run tempfocus once; it avoids the larger uncertainty in the zero point for the function. The scripts log temperature and focus values, to keep broadening the range of validity of the function.
NEW seeing measurements:
The results show that the image quality improved significantly after the new mirror was installed in September 2013:
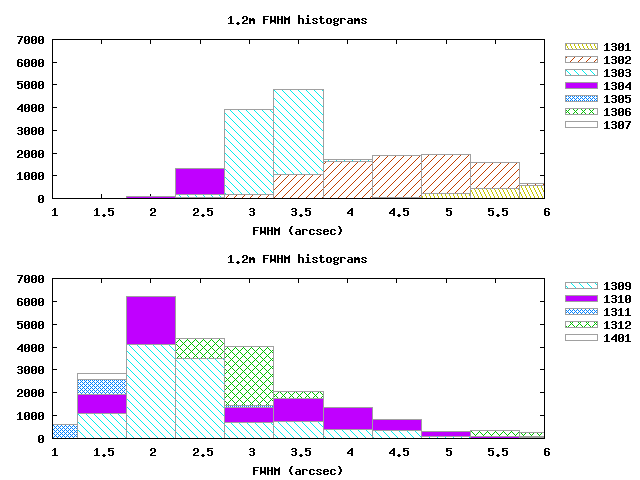
The quality was better in the first half, compared to the second half, of 2014:
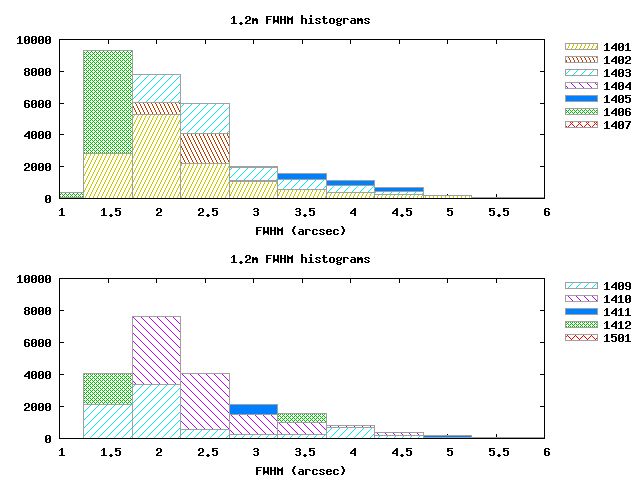
The quality was again better in the first half of 2015, but the onset of El Niño made the second half significantly worse:
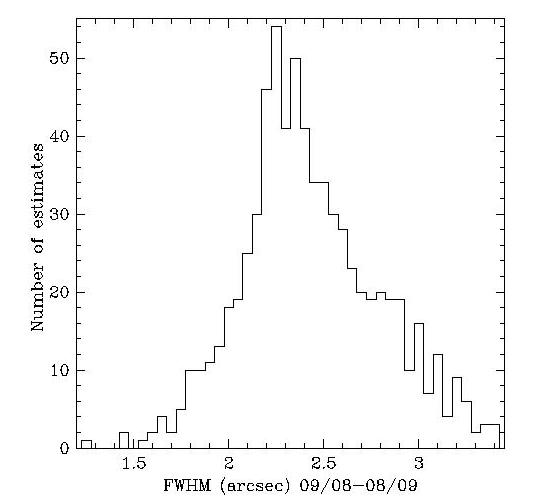
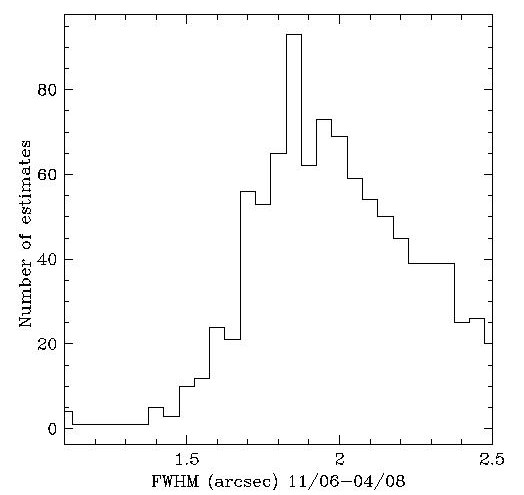
Old calibrations and seeing measurements:
Consistent with Deb Woods' 2006
WFS analysis of the 1.2m primary,
the seeing we measure with Keplercam and the r filter
has deteriorated compared to previous measurements:
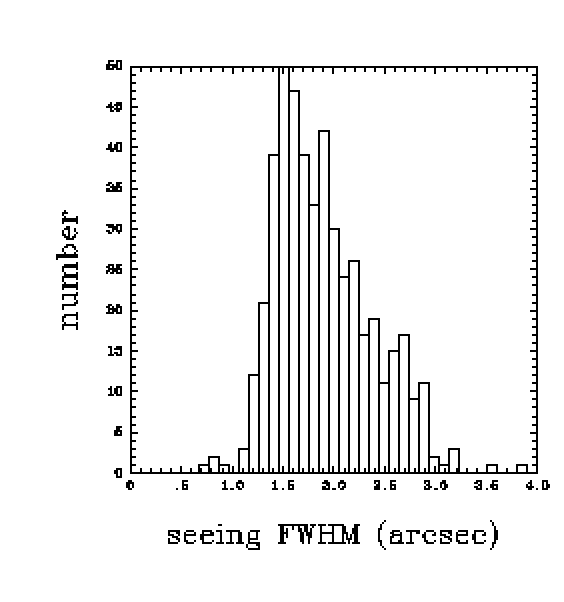
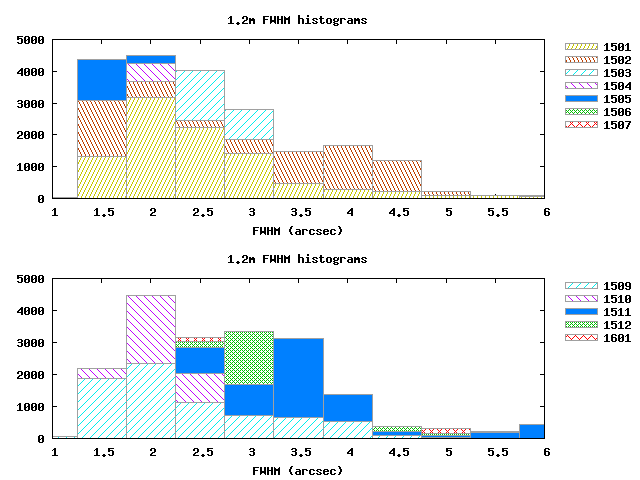
Minicam calibration:
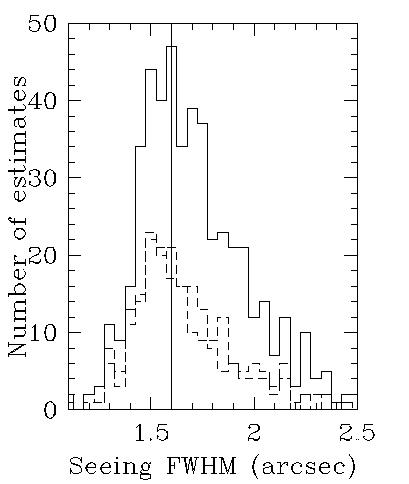
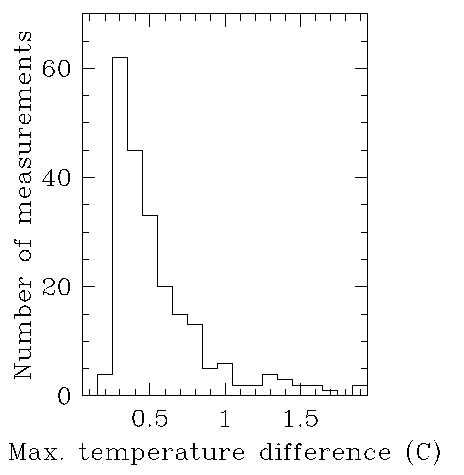
The solid histogram includes all the measurements, while the dashed histograms show measurements taken when the temperature difference between the mirror and the chamber was below 0.5C, or when the measurements were made in the middle of the night. The different histograms show little difference in the median seeing of about 1.6 arcsec. The plot below is a histogram of the maximum temperature difference between sensors on the mirror and sensors in the chamber. The peak is at 0.3C.
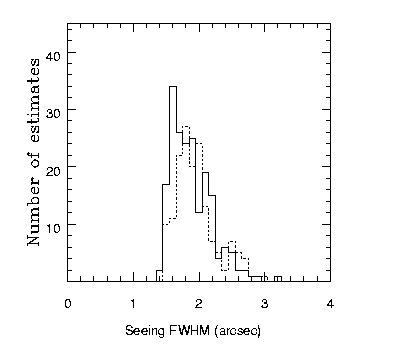
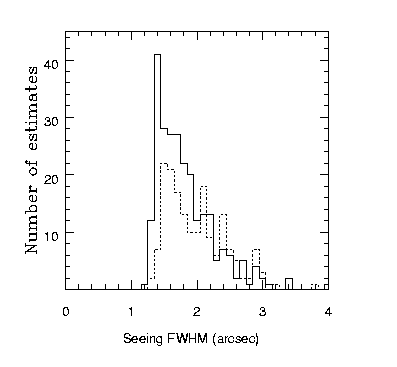
The two histograms above show there are interesting differences for data taken with the old pod and the new hexapod :
The first two items above indicate there was some improvement in the 1.2m seeing thanks to the hexapod. Work will continue to try to improve the seeing further.